Data Product in FP&A
Data Governance as the Foundation for Data-Driven Decision Making
Listening to a 22 March DataFramed podcast episode on Data Governance got me thinking about data as a product in FP&A. Last year I wrote about FP&A itself as a product. Data Product concept seems to me a relevant enabler. Below are then my thoughts and summaries as usual, trying to connect data product idea to the different concepts I tend to go back to.
Outline for today:
Summary of the DataFramed podcast on Data Governance
Data Product Concept in FP&A
What is a Data Governance Framework
Promoting Data Literacy and Skills Development
Creating the Conditions for Data Product thinking and Data-Driven Decision-Making
Before jumping into the text, then why do write? Because of this:
While we naturally understand that writing is a good way to share ideas with others, we under-appreciate just how much good writing helps us think about an idea ourselves. Writing is not only a means of communication, it enables us to practice reasoning. - Shane Parrish at fs.blog
I. Summary of the DataFramed podcast on Data Governance
The DataFramed podcast featuring Saurabh Gupta from The Modern Data Company provided valuable insights into data governance and its role in today's data-centric organizations. Gupta emphasized the importance of embedding data governance early in the data lifecycle and advocated for a proactive approach to data quality management in order to leverage data for effective decision-making.
Key Insights
Embedding Data Governance Early: Gupta stresses the importance of integrating data governance initiatives at the earliest stages of the data lifecycle to ensure data quality and compliance.
Proactive Data Quality Management: The conversation advocates for 'shifting left' in data quality checks to identify and rectify issues promptly, enhancing overall data usability and trustworthiness.
The Strategic Role of Data Product Managers: Highlighting the emergence of Data Product Managers, Gupta underscores their pivotal role in fostering a seamless bridge between data’s production and its strategic use, ensuring data not only meets quality standards but also aligns with organizational objectives.
Fostering Collaboration and Standardization: The podcast points to the necessity of forging strong collaborations between different stakeholders in the data ecosystem and standardizing data governance practices across the organization to streamline operations and decision-making processes.
Navigating the Future with Generative AI: Reflecting on the advent of generative AI, Gupta elucidates on the foundational need for a solid data governance strategy to fully leverage the potential of advanced analytics and AI technologies for informed decision-making.
Cultivating a Culture of Continuous Improvement: Lastly, Gupta calls for an organizational culture that values continuous improvement, iterative development, and a collaborative approach to data governance, ensuring that frameworks evolve in tandem with technological advancements and business needs.
By prioritizing data governance from the get-go, fostering a culture of collaboration, and embracing the role of Data Product Managers, organizations can significantly enhance the quality, security, and usability of their data. This not only paves the way for leveraging advanced data analytics and AI but also ensures that data-driven decision-making becomes a core competency within the organization.
The insights offered by Gupta provide a valuable roadmap also for FP&A professionals and organizations at large, aiming to harness the full potential of their data assets.
II. Data Product Concept in FP&A
In the evolving landscape of Financial Planning and Analysis (FP&A), data has emerged as a critical asset that fuels strategic decision-making. As organizations increasingly rely on data-driven insights, the importance of robust data governance and a product-centric approach to data management has become more evident than ever before.
Key Concepts
Shifting Left: Integrating Data Quality Checks Early The concept of "shifting left" involves incorporating data quality checks at the beginning of the workflow. By identifying and rectifying data discrepancies early on, FP&A professionals can ensure the reliability of their forecasts and analyses. This proactive approach not only saves time but also establishes a foundation of trust and credibility in FP&A reporting.
The Emergence of Data Product Managers in FP&A: The role of Data Product Managers is becoming increasingly relevant in FP&A. These professionals act as the architects behind ensuring that financial models and analyses are based on meticulously curated and governed data. By treating data as a product—aligned with strategic objectives and subject to rigorous quality control—Data Product Managers elevate data to a structured asset that informs sound financial planning.
Developing a Data Governance Framework for FP&A: To navigate the complexities of data management, FP&A teams must develop and actively work with a comprehensive data governance framework. This blueprint should clearly define ownership of financial data sets, establish quality control measures, and foster a culture where data is respected and protected from manipulation. By embedding these governance principles into daily operations, FP&A professionals can enhance the accuracy and strategic value of their financial insights.
Collaboration: The Key to Data Excellence Achieving data excellence in FP&A is a collaborative endeavor that requires strong partnerships between IT, data management teams, and FP&A professionals. By working together to ensure data quality, accessibility, and actionability, organizations can unlock the full potential of their data assets. Celebrating quick wins, such as showcasing the benefits of a transparent and efficient data governance framework, can help rally support for these efforts.
The data product concept is transforming the way FP&A teams approach data management and decision-making. By shifting data quality checks to the beginning of the workflow, embracing the role of Data Product Managers, developing a robust data governance framework, and fostering collaboration, organizations can harness the strategic value of their data. As FP&A professionals embrace this mindset, they can drive more accurate and insightful financial planning, ultimately contributing to the organization's success in a data-driven world.
III. What is a Data Governance Framework
A Data Governance Framework serves as the backbone of an organization's data management strategy. It encompasses a set of policies, procedures, and standards that ensure data accuracy, security, and effective utilization. Understanding and implementing a robust Data Governance Framework is crucial for FP&A professionals to unlock the full potential of their data assets and drive informed decision-making.
Key Concepts
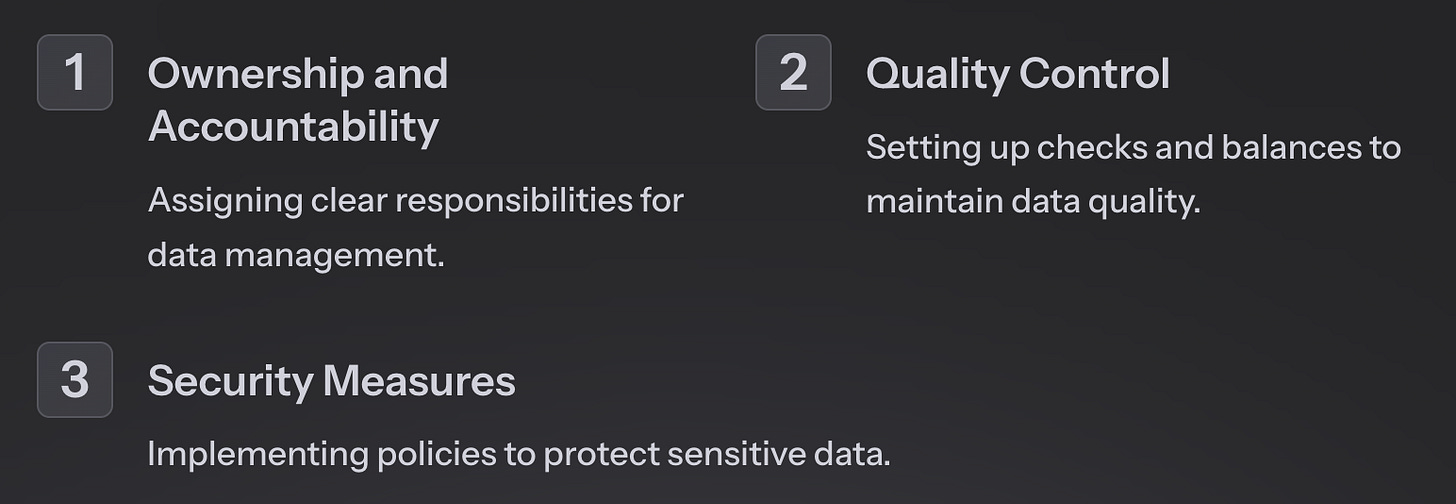
Ownership and Accountability: A fundamental aspect of a Data Governance Framework is assigning clear responsibilities for data management. This involves identifying data owners, stewards, and custodians, ensuring that everyone understands their roles and responsibilities. By establishing a sense of ownership and accountability, organizations can foster a culture of data stewardship and maintain data integrity.
Quality Control and Data Integrity: Implementing rigorous quality control measures is essential to maintain the accuracy and reliability of financial data. A Data Governance Framework should outline processes for data validation, reconciliation, and error handling. By establishing standardized data quality checks and balances, FP&A teams can ensure that their analyses and forecasts are based on trustworthy data, leading to more confident decision-making.
Data Security and Compliance: Safeguarding sensitive financial data is a top priority for any organization. A Data Governance Framework should incorporate robust security measures, access controls, and data protection policies. It should also address compliance with relevant legal and regulatory standards, such as GDPR or industry-specific regulations. By prioritizing data security and compliance, FP&A teams can mitigate risks and maintain the confidentiality and integrity of financial information.
Data Lifecycle Management: Effective data governance extends throughout the entire data lifecycle, from acquisition to retirement. A Data Governance Framework should define processes for data collection, storage, archiving, and eventual deletion. By establishing clear guidelines for data lifecycle management, organizations can optimize data storage costs, ensure data relevance, and comply with data retention policies.
Metadata Management and Data Lineage: Metadata management involves documenting and organizing information about data, such as its definition, source, and relationships. Data lineage, on the other hand, tracks the movement and transformation of data across systems. A Data Governance Framework should incorporate metadata management and data lineage practices to enhance data transparency, traceability, and understanding. This enables FP&A professionals to trace the origin of data, understand its context, and make informed decisions based on reliable information.
A well-designed Data Governance Framework is a critical asset for FP&A teams in today's data-driven landscape. By establishing clear ownership, implementing quality control measures, prioritizing data security and compliance, managing data throughout its lifecycle, and leveraging metadata and data lineage, organizations can unlock the true value of their financial data. Embracing a robust Data Governance Framework empowers FP&A professionals to make informed decisions, drive strategic initiatives, and contribute to the overall success of the organization.
IV. Promoting Data Literacy and Skills Development
Before we take it for granted that putting in place a new framework or process = success, we need to come back to the basics, i.e. how will our people know what to make of the new tools and expectations. So, boosting data literacy is key to empowering the team to make informed decisions and fostering a culture where data drives strategy.
Key Concepts
Assessing and Addressing Data Literacy Gaps: The first step in promoting data literacy is to understand the current skill levels within the FP&A team. Conducting surveys or assessments can help identify gaps in data literacy and pinpoint areas where training and development efforts should be focused. By tailoring training initiatives to meet specific needs, organizations can ensure that everyone has the foundation they need to succeed in a data-driven environment.
Creating Engaging Training Programs: To effectively upskill FP&A professionals, it's essential to design engaging and relevant training programs. This can involve a mix of interactive workshops, e-learning modules, community-based learning, and bite-sized tutorials. By offering a variety of learning formats, organizations can cater to different learning styles and ensure broader reach and engagement. Role-specific training, ranging from the basics of data handling to mastering analytics tools, can further enhance the relevance and applicability of the skills acquired.
Fostering Practical Application and Knowledge Sharing: Encouraging hands-on learning is crucial for cementing data literacy skills. By integrating real data challenges into projects, FP&A professionals can apply their newly acquired knowledge in real-world scenarios. Additionally, creating a community of practice, where data champions can mentor and inspire their peers, promotes knowledge sharing and continuous learning. This collaborative approach not only reinforces data literacy but also fosters a culture of innovation and teamwork.
Embedding Data Literacy in the Organizational DNA: To truly embrace data literacy, it must become an integral part of the organization's DNA. This involves making data literacy a key component of onboarding processes and continuous professional development, aligning it with career growth paths. By showcasing success stories where data-driven decisions have made a significant impact, organizations can reinforce the value of data literacy and secure buy-in from all levels of the organization.
Leveraging Expertise and Tools: Organizations should tap into the wealth of knowledge both within and outside their walls. Inviting experts to share insights and introducing employees to the latest trends and tools in data analytics can broaden their horizons and inspire innovation. Providing access to intuitive analytics platforms and support resources further encourages experimentation and exploration, enabling FP&A professionals to apply their data literacy skills in practice.
Promoting data literacy and skills development is a critical component of embracing data governance and the data product mindset in FP&A. By assessing and addressing data literacy gaps, creating engaging training programs, fostering practical application, embedding data literacy in the organizational DNA, and leveraging expertise and tools, organizations can empower their FP&A teams to make informed decisions and drive strategic initiatives. By investing in data literacy, organizations can unlock the full potential of their data assets and cultivate a culture of data-driven excellence.
V. Building a Culture of Data Product Thinking and Data-Driven Decision Making
As culture eats strategy and new processes for breakfast, I’ll try to put together what the current blogpost tries to promote (Data Product in FP&A) with the systems thinking and organizational learning topics I fall back on almost every time.
By weaving together insights from the DataFramed podcast on Data Governance, Peter Senge's "The Fifth Discipline," and Donella Meadows' "Thinking in Systems," we can cultivate an environment where data is not just an asset, but a catalyst for strategic decision-making and innovation.
Key Concepts
Adopting Systems Thinking: Systems thinking encourages us to view data as an interconnected part of our organizational ecosystem. By breaking down silos and fostering collaboration, FP&A professionals can leverage data's full potential. This holistic approach transforms data governance from a mere compliance activity into a strategic enabler, driving informed decision-making across the organization.
Cultivating a Shared Vision: Uniting everyone behind a common goal of harnessing data for insightful decision-making and forecasting is crucial. When data governance evolves from a mandate to a shared mission, it ignites a sense of purpose and commitment. This collective vision, echoed in the insights from our podcast guests, serves as a guiding light, empowering FP&A teams to contribute meaningfully to the organization's success.
Championing Personal Mastery and Team Learning: Investing in continuous data literacy and analytics skills development is key to fostering a culture of data product thinking. By empowering individuals to grow and innovate, we create an agile and informed FP&A team, ready to adapt to the ever-changing business landscape. Encouraging a growth mindset and providing opportunities for personal mastery, as emphasized by Senge, ensures that our team remains at the forefront of data-driven decision-making.
Promoting a Data-as-a-Product Mentality: Treating data with the same rigor as a product aligns perfectly with Meadows' systems thinking approach. By focusing on data quality, reliability, and user experience, we elevate data governance from a control mechanism to a value-creation engine. This mentality enhances the quality of financial planning and analysis outputs, driving more accurate and actionable insights.
Leading by Example: Leadership plays a pivotal role in modeling data-driven decision-making. When senior leaders demonstrate their commitment to data governance and leverage insights for strategic decisions, it sets a powerful precedent for the entire organization. By walking the talk, leaders can inspire a culture where data is respected, valued, and effectively utilized.
So then, embedding a culture that values data product thinking and data-driven decision making is pivotal for the success of FP&A functions. It demands an organization-wide effort, underpinned by
systems thinking
a shared vision for data's role in driving business value, and
an unwavering commitment to personal and team development (not osmosis-learning).
By this cultural shift, organizations can harness their data assets more effectively, paving the way for innovation, efficiency, and a substantial competitive edge in the data-rich world of finance. Let’s put our data into use!